Are you a business owner looking to secure funding or establish partnerships? If so, you’ve probably come across the term “business credit score” in your research. Understanding what a business credit score is and how it works is crucial for the success of your company. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of business credit scores, addressing the problems they solve and offering valuable solutions. So, let’s accept the challenge and explore the world of business credit scores together!
As a business owner, you may face difficulties in obtaining loans, lines of credit, or favorable terms with suppliers. These challenges often arise due to a lack of understanding about the importance of a business credit score. Without a solid credit score, your business may be perceived as a financial risk, hindering growth opportunities and making it harder to compete in the market.
But worry not! We are here to guide you through the maze of business credit scores and provide effective solutions to improve and maintain a healthy credit standing for your company. By the end of this blog post, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what a business credit score entails and the steps you can take to optimize it.
What Is a Business Credit Score?
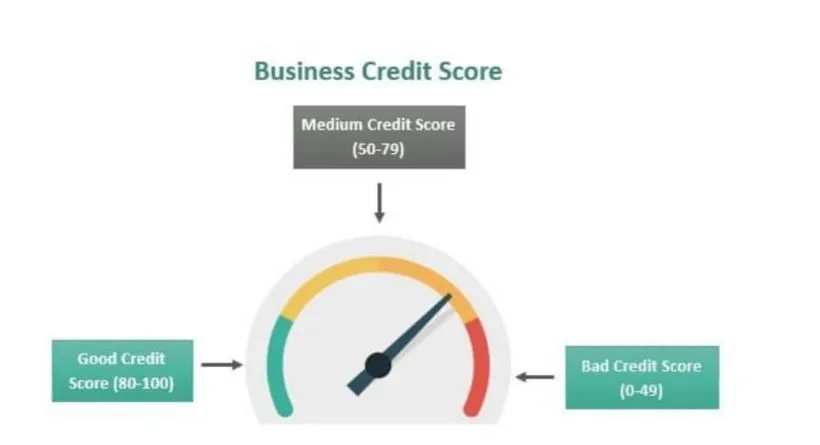
Definition and Significance of a Business Credit Score
When it comes to assessing the financial health and credibility of a business, a business credit score plays a vital role. Similar to a personal credit score, a business credit score is a numerical representation of a company’s creditworthiness. It serves as a measure of how likely a business is to fulfill its financial obligations, such as repaying loans and lines of credit.
Having a strong business credit score is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it instills confidence in lenders and suppliers, as it reflects your ability to manage and fulfill financial commitments. A good credit score can open doors to better financing options, lower interest rates, and more favorable terms. Additionally, it can enhance your reputation in the marketplace, attracting potential partners and stakeholders who value financial stability.
Comparison with Personal Credit Scores
While personal credit scores assess an individual’s creditworthiness, business credit scores focus specifically on the financial reputation of a company. They take into account factors such as payment history, credit utilization, public records, and length of credit history.
It’s important to understand that personal credit scores and business credit scores are separate entities. Even if you have an excellent personal credit score, it doesn’t automatically translate to a strong business credit score. The two are evaluated differently and have distinct implications for their respective contexts. Therefore, as a business owner, it’s crucial to establish and maintain a separate business credit profile to maximize your chances of securing favorable financing and business opportunities.
Explanation of How Business Credit Scores Are Calculated
Business credit scores are calculated based on various factors, each carrying a specific weight in the evaluation process. While the exact algorithms used by credit reporting agencies may differ slightly, some common elements are typically considered:
- Payment History: Timely payments to creditors and suppliers are vital for maintaining a good credit score. Consistently meeting your financial obligations demonstrates reliability and financial responsibility.
- Credit Utilization Ratio: This measures the percentage of available credit that a business is utilizing. It’s advisable to keep the credit utilization ratio low, as high utilization can signal potential financial strain.
- Length of Credit History: The longer a business has a credit history, the more data lenders and credit agencies have to assess its financial behavior. A longer credit history allows for a more accurate evaluation of creditworthiness.
- Public Records: Negative public records, such as bankruptcies, liens, or judgments, can significantly impact a business credit score. Avoiding these adverse events is essential for maintaining a strong credit profile.
Introduction to Key Credit Reporting Agencies
Several credit reporting agencies specialize in assessing and reporting business credit scores. These agencies gather data from various sources, including creditors, public records, and other financial institutions. Some of the most prominent credit reporting agencies include Dun & Bradstreet, Experian Business, Equifax Small Business, and Credit Safe.
These agencies compile information about your business and generate credit reports and scores based on their assessment. Lenders, suppliers, and other stakeholders often rely on these reports when making decisions about providing credit or entering into business relationships.
Factors That Influence Business Credit Scores
Payment History and Its Impact on Credit Scores
Your business’s payment history holds significant weight when it comes to calculating your business credit score. Lenders and credit agencies closely examine how promptly you make payments to creditors and suppliers. Consistently paying your bills on time demonstrates financial responsibility and reliability, positively impacting your credit score.
To ensure a strong payment history, it’s crucial to prioritize timely payments. Consider setting up automated reminders or utilizing online banking tools to streamline the payment process. By staying on top of your financial obligations, you’ll not only maintain a positive credit score but also build a reputation as a dependable business partner.
Credit Utilization Ratio and Managing Debt Effectively
The credit utilization ratio is another crucial factor that influences your business credit score. This ratio measures the percentage of your available credit that you’re utilizing at any given time. Keeping this ratio low is advisable, as it indicates that your business is managing its debt responsibly and not overly reliant on credit.
For example, if your business has a credit limit of $10,000 and your outstanding balances total $2,000, your credit utilization ratio would be 20%. Aim to keep your ratio below 30% to maintain a favorable credit score. By managing your debt effectively and keeping your credit utilization in check, you demonstrate financial stability and reduce the risk perceived by lenders.
Length of Credit History and Its Role in Building Credibility
The length of your business’s credit history is an essential factor in determining your creditworthiness. Lenders and credit agencies assess how long you have been using credit to evaluate your financial behavior and credibility. A longer credit history provides a more comprehensive picture of your financial management skills.
If your business is relatively new, building a credit history takes time and patience. Consider establishing relationships with vendors or suppliers who report payments to credit bureaus. These reported transactions will contribute to your credit history, gradually bolstering your business credit score. Remember, the longer your credit history, the stronger your credibility becomes in the eyes of lenders and suppliers.
Public Records and Their Implications for Credit Scores
Public records, such as bankruptcies, liens, or judgments, can significantly impact your business credit score. These records indicate potential financial challenges or legal issues, raising concerns among lenders and creditors. Negative public records can lower your credit score and make it harder to secure favorable financing options.
It’s crucial to avoid or address any public records that may tarnish your credit profile. Regularly monitor your business’s financial standing and address potential issues promptly. By taking proactive measures to resolve financial and legal challenges, you protect your credit score and maintain a positive reputation.
Other Factors Affecting Business Credit Scores
In addition to the aforementioned factors, several other elements can influence your business credit score. While the exact algorithms used by credit reporting agencies may vary, some common considerations include the number and types of credit accounts your business has, any recent credit applications or inquiries, and the diversity of your credit portfolio.
By being aware of these various factors and their impact on your business credit score, you can strategically manage your finances and take steps to improve your creditworthiness. In the next section, we will explore practical strategies and tips to enhance and maintain a healthy business credit score. So, let’s delve into the actionable steps you can take to boost your financial standing and unlock opportunities for your business.
Strategies to Improve and Maintain Your Business Credit Score
Monitoring and Reviewing Your Credit Reports Regularly
Regularly monitoring and reviewing your business credit reports is essential for maintaining a healthy credit score. By staying informed about your credit standing, you can identify any errors, inaccuracies, or potential issues that may negatively impact your score. Reviewing your reports also allows you to detect any signs of fraudulent activity or identity theft.
To monitor your credit reports, consider subscribing to credit monitoring services or utilizing online platforms that provide access to your credit information. Set a schedule to review your reports at least annually or even more frequently if you anticipate significant financial changes or credit applications. By staying proactive and vigilant, you can address any discrepancies promptly and ensure the accuracy of your credit profile.
Establishing a Solid Credit History and Payment Track Record
Building a solid credit history is a key factor in improving and maintaining your business credit score. Start by establishing relationships with vendors, suppliers, or service providers who report your payment history to credit bureaus. Consistently making payments on time and in full demonstrates your reliability and financial responsibility.
One effective strategy is to start small by obtaining a business credit card or a small line of credit. Make regular purchases and diligently repay the balances on time, gradually building a positive payment track record. Remember, each timely payment contributes to strengthening your creditworthiness and improving your business credit score over time.
Managing Your Business’s Financial Obligations Responsibly
Responsible financial management is crucial for maintaining a healthy business credit score. This includes managing your business’s financial obligations effectively, such as loans, lines of credit, and trade credit with suppliers. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of your payment terms and obligations, and budget accordingly to meet these obligations on time.
Keep a close eye on your cash flow and strive to maintain a consistent payment schedule. A steady and predictable payment pattern enhances your creditworthiness and demonstrates financial stability. Consider implementing automated payment systems or setting up reminders to avoid any unintentional delays in fulfilling your financial obligations.
Building Relationships with Suppliers and Creditors
Building strong relationships with your suppliers and creditors can positively impact your business credit score. Cultivate open and transparent communication with them, especially when facing financial difficulties or unexpected challenges. Proactively discuss potential solutions, such as renegotiating payment terms or exploring alternative financing options.
Maintaining positive relationships with suppliers and creditors can lead to greater flexibility during challenging times, such as offering extended payment terms or providing financial support when needed. These relationships can also result in positive references or recommendations, further bolstering your business’s creditworthiness.
Tips for Recovering from a Low Credit Score
If your business credit score is currently low, don’t despair. With time and effort, it is possible to improve your creditworthiness. Start by addressing the underlying issues that contributed to the low score. Analyze your credit reports, identify any negative factors, and develop a plan to rectify them.
Some practical tips for recovering from a low credit score include:
- Paying all bills on time, even if it means making minimum payments.
- Reducing your credit utilization ratio by paying down existing debts.
- Working with creditors to negotiate repayment plans or settlements.
- Building a positive payment history by establishing new credit accounts and making timely payments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and actively managing your business credit score is crucial for the long-term success and growth of your company. A good credit score opens doors to a wide range of benefits, including access to favorable financing options, building trust with suppliers, and enhancing your credibility in the marketplace.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition and significance of a business credit score, delved into the factors that influence it, and provided strategies to improve and maintain a healthy credit profile. By monitoring your credit reports regularly, establishing a solid payment track record, managing your financial obligations responsibly, and building strong relationships with suppliers and creditors, you can make significant strides in improving your creditworthiness.

